Human trafficking can occur anywhere. Traffickers can be any race, ethnicity, or social status, but they prey on people in difficult situations. You are going to view a series of 4 videos and images of real cases that have occurred in the United States. Walking through these scenarios will strengthen your ability to identify the crimes of human trafficking and recognize that there are serious consequences for these crimes under the law. How well do you think you know the consequences that traffickers face? Let’s find out! Before you start, take a quick look at the federal statutes against human trafficking and the flow chart that provides a glimpse on the consequences imposed on those convicted of these heinous crimes. Make a mental note of how different human trafficking crimes might yield similar or different consequences for the trafficker. When you have finished reviewing the information below, click next to continue to the videos.
Human trafficking crimes are defined in Title 18, Chapter 77 of the United States Criminal Code and include the following: (https://www.justice.gov/crt/human-trafficking-prosecution-unit-htpu)
- 18 U.S.C. § 1581 (Peonage)
- 18 U.S.C. § 1584 (Involuntary Servitude)
- 18 U.S.C. § 1589 (Forced Labor)
- 18 U.S.C. § 1590 (Trafficking with Respect to Peonage, Slavery, Involuntary Servitude, or Forced Labor)
- 18 U.S.C. § 1591 (Sex Trafficking of Children or by Force, Fraud, or Coercion)
- 18 U.S.C. § 1592 (Unlawful Conduct with Respect to Documents in Furtherance of Trafficking, Peonage, Slavery, Involuntary Servitude, or Forced Labor)
- 18 U.S.C. § 1593 (Mandatory Restitution)
- 18 U.S.C. § 1594 (Attempt and Forfeiture)
- 18 U.S.C. § 1595 (Private Right of Action)
- 18 U.S.C. § 2423 (Transportation of Minors into Prostitution)
These statutes are rooted in the prohibition against slavery and involuntary servitude guaranteed by the Thirteenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution. “Neither slavery nor involuntary servitude, except as a punishment for crime whereof the party shall have been duly convicted, shall exist within the United States, or any place subject to their jurisdiction.”
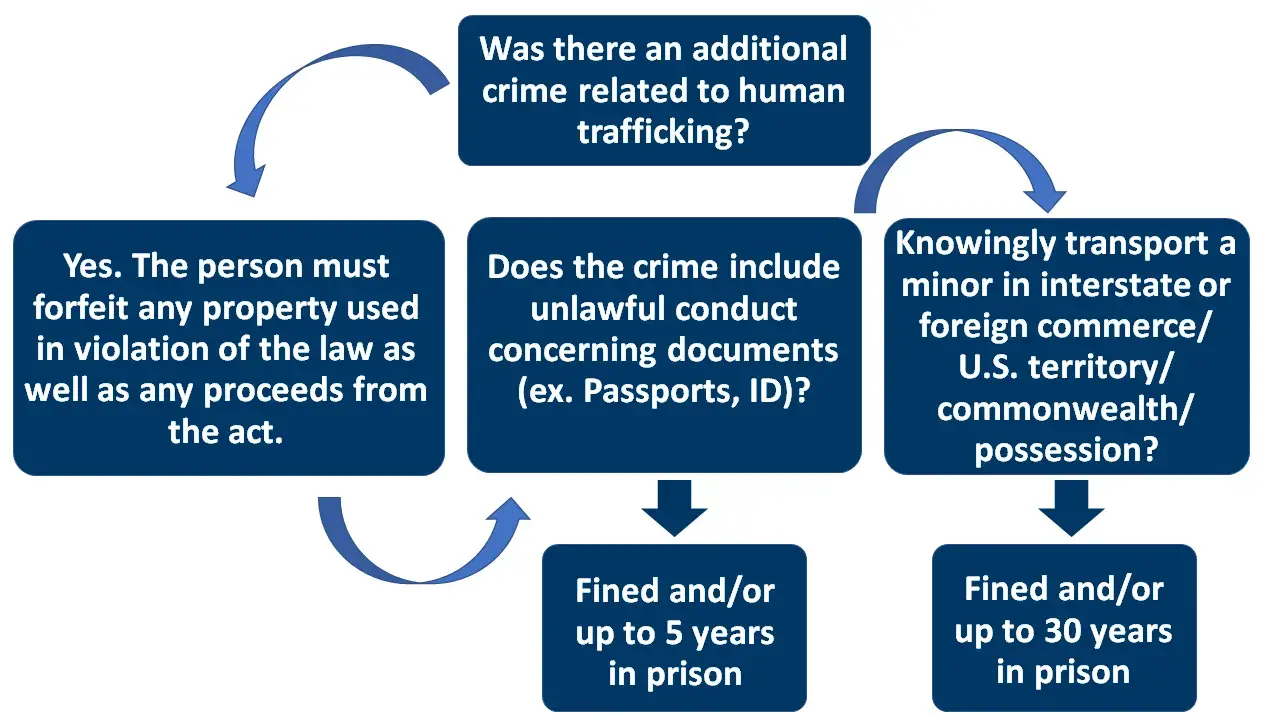
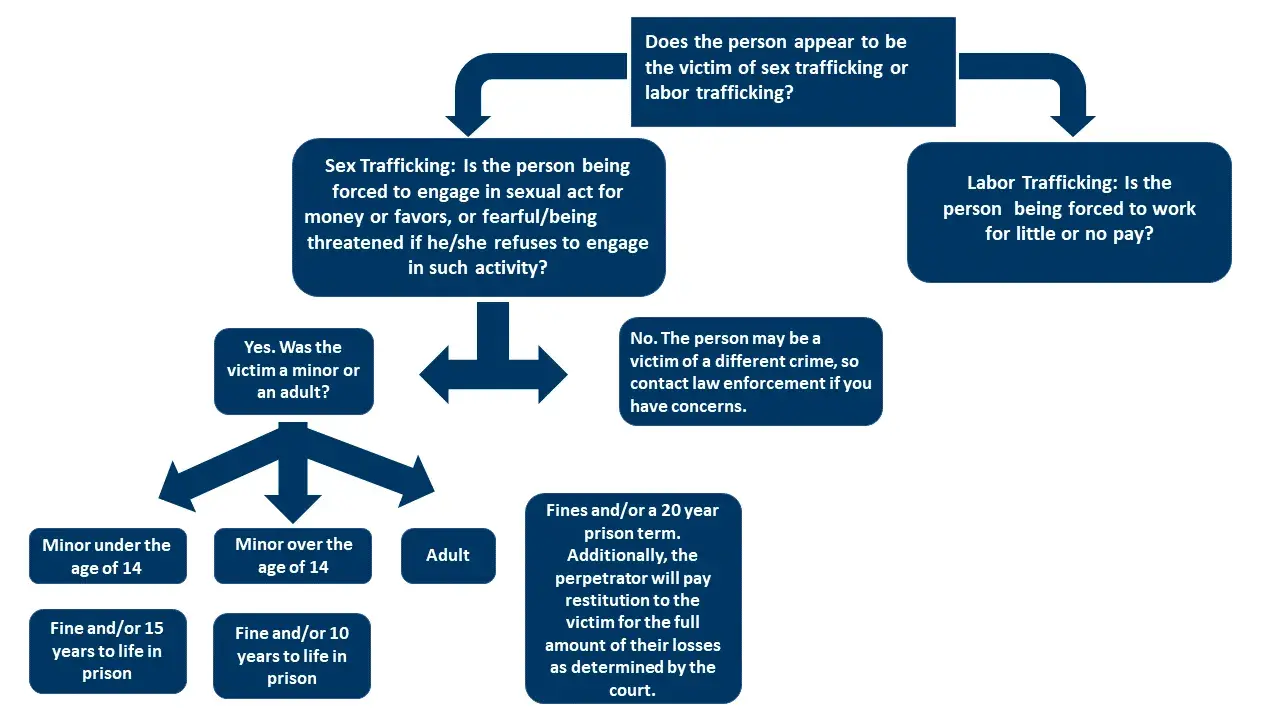
Human Trafficking is a FEDERAL crime. By law, persons who commit labor or sex trafficking crimes are subject to certain penalties. Use this flowchart to learn more.
 x
x