The Countering Weapons of Mass Destruction (CWMD) Office was established in December 2017 by consolidating primarily the Domestic Nuclear Detection Office, a majority of the Office of Health Affairs, as well as other DHS elements.
For current information related to CWMD, please visit the following:
The Department of Homeland Security coordinated the development of and accepted American National Standards Institute (ANSI) / Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) N42 consensus standards for six (6) categories of radiation detection equipment. Manufacturers and vendors previously submitted detectors through the Department of Homeland Security Office of Science and Technology (S&T) for testing against these ANSI/IEEE standards in 2005 and 2006. None of the detectors tested under that program met all of the consensus standard requirements.
The Domestic Nuclear Detection Office (DNDO) is now responsible for coordinating federal efforts to detect and protect against the unauthorized importation, possession, storage, transportation, development, or use of a nuclear explosive device, fissile material, or radiological material in the United States. Sec. 1902 of the Homeland Security Act of 2002, Pub. L. No. 107-296, added by Sec. 501 of the Security and Accountability For Every (SAFE) Port Act, and renumbered by Pub. L. No. 110-53, directs the Department of Homeland Security Domestic Nuclear Detection Office to "carry out a program to test and evaluate technology for detecting a nuclear explosive device and fissile or radiological material..."
The Graduated Radiation/Nuclear Detector Evaluation and Reporting (GRaDERSM) Program provides a means of independently testing and evaluating (T&E) commercially available radiological and nuclear (Rad/Nuc) detection equipment against ANSI/IEEE N42 performance standards to enhance the confidence in radiation detector capabilities for systems funded by government procurement and grant programs. GRaDER will provide performance and operationally relevant technical information on these systems to Department components, and state, local, tribal, and territorial governments and first responders.
Primary Objectives
The primary objectives of GRaDER are to:
- Encourage manufacturers to develop better radiation detection and identification products that satisfy consensus standards, government-unique technical capability standards, and evolving Homeland Security mission requirements.
Develop a test program that will provide data needed to make radiation detection device acquisition and funding decisions, and identify the radiation detection and identification products available that satisfy consensus standards and Homeland Security mission architecture requirements. - Standardize instrument testing and test results reporting to assure valid comparisons and easily interpreted reports.
- Develop an easily interpreted display of key test results that may be made available to stakeholders, such as state and local users.
- Provide the infrastructure for the development of high integrity test data.
- Develop a Government Post-Market Surveillance (GPMS) program to track product quality and market experience with instruments already evaluated in the GRaDER program.
Testing and Evaluation Process
The testing process includes two phases.
GRaDERSM Program Overview
Radiation/Nuclear Detectors for Prevention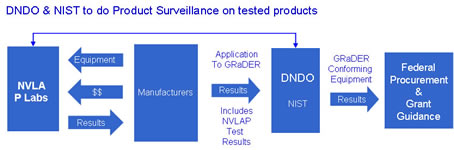
The first phase will involve testing by DNDO accepted laboratories and/or laboratories accredited by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) National Voluntary Laboratory Accreditation Program (NVLAP) accreditation process against existing unclassified, consensus-based ANSI/IEEE N42 standards. Subsets of the requirements in these consensus standards will be used to determine DNDO compliance levels. These subsets emphasize radiation detection performance first and then environmental and operational capabilities and limitations.
The second phase will entail testing at DNDO accepted government facilities against threat based Government-Unique Technical Capability Standards (GUS) (to be published), and sources under realistic operational and environmental conditions.
In addition to these two phases of GRaDER testing, DNDO will implement a product surveillance program that will be coordinated by NIST. This will involve subsequent post-market testing and assessments of radiation detectors that have already been tested and evaluated under the GRaDER Program. Results of these post-market assessments may impact the standing of the radiation detectors identified within the GRaDER Program and be used to further inform the GRaDER Program stakeholders, the ANSI and GUS developers.
All testing is voluntary and at the manufacturer's expense.
Reporting Conventions - Compliance Levels
Results of compliance testing and DNDO analysis will be summarized under compliance levels. The GRaDER Program compliance levels and criteria for achieving these compliance levels are outlined on the GRaDER webpage entitled Compliance Levels for GRaDER Instrument Performance.
Observations from testing that relate to radiation detector suitability for DHS missions and environmental conditions will be captured in comment form and will be provided for the consideration of the GRaDER stakeholders.
Manufacturers may elect to have their test results included in a DNDO-published listing made available to interested parties outside the federal government. This listing may be used by federal, state and local authorities in making procurement and grant decisions. If a manufacturer does not agree to such publication, the test results will not be released outside the federal government. The incentive to participate comes from government procurement and grant programs award criteria. Only equipment that meets the designated criteria will receive government funding.
Application Process
Manufacturers initiate the GRaDER test and evaluation process by contracting with the appropriate laboratory to initiate testing against the applicable ANSI N42 consensus standard. Once acceptable test results have been attained, the manufacturer applies to DNDO for consideration of its radiation detector product in the GRaDER Program.
Manufacturers' GRaDER Program applications are submitted to DNDO under company letterhead. Criteria for entry into the GRaDER Program include satisfactory demonstration of compliance with applicable subsets of the ANSI N42 Standards' requirements as outlined in the Compliance Levels section of the initial GRaDER Guidance Notice. Demonstration of compliance with the consensus standards may be achieved in either of two methods. The first method is with an original independent test report from a NVLAP-accredited laboratory for testing against the ANSI N42 Standards. The second method is with an original independent test report from a DNDO-accepted testing laboratory. The conformity requirements outlined in the Test and Evaluation Interest Areas section must also be satisfied.
Applications must be complete at time of submission. Independent reports and certifications must be verifiable with the originating organizations. DNDO will attempt to resolve omissions and other problems directly with manufacturers as rapidly as possible. However, the government reserves the right to return incomplete applications without further action if omissions and requests for clarification are not resolved within 30 days of receipt.
Additional application guidance is provided with the GRaDERSM Program Guidance Checklist for Submitting Manufacturers' Applications (PDF, 4 pages - 20 KB). The GRaDERSM Program Product Listing Agreement must be signed, dated, and included in the manufacturer's application packet along with the completed aforementioned checklist document.
Test and Evaluation Interest Areas
Learn more about the re-testing process
A complete and independently verifiable detector configuration description must be provided with the application, to include software and firmware version identification and instructions. Applications must include manufacturer or vendor points of contact names, mailing and shipping addresses, telephone number, and electronic mail addresses.
DNDO requires that manufacturers provide information relating to conformance to other industry and government standards, including those identified below. The GRaDER Program examines certifications from recognized organizations and agencies, and original signed declarations of conformity to these standards. GRaDER verification may include audit and/or testing at the government's discretion, and as part of the GRaDER post-market surveillance program.
Training Capabilities. DNDO assesses the manufacturer provided training capabilities and materials as part of the government-unique technical capability standards phase of GRaDER testing. DNDO uses portions of ANSI N42.37-2006 American National Standard for Training Requirements for Homeland Security Purposes Using Radiation Detection Instrumentation for Interdiction and Prevention as the standard with which to evaluate training.
Electrical Safety. Electrical equipment that is intended to be used in a regulated workplace will be "certified" to the appropriate safety requirements by an Occupational Safety and Health (OSHA)-accredited Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL), under the applicable General Industry Standards (Part 1910 of Title 29, Code of Federal Regulations - 29 CFR Part 1910). Please visit OSHA for a listing of NRTL facilities:
http://www.osha.gov/dts/otpca/nrtl/index.html
GRaDER compliance verification for these Test and Evaluation interest areas may include audit and/or testing at the government's discretion, and as part of the GRaDER post-market surveillance program. Any additional costs for government verification of conformity will be at the manufacturer's expense.
